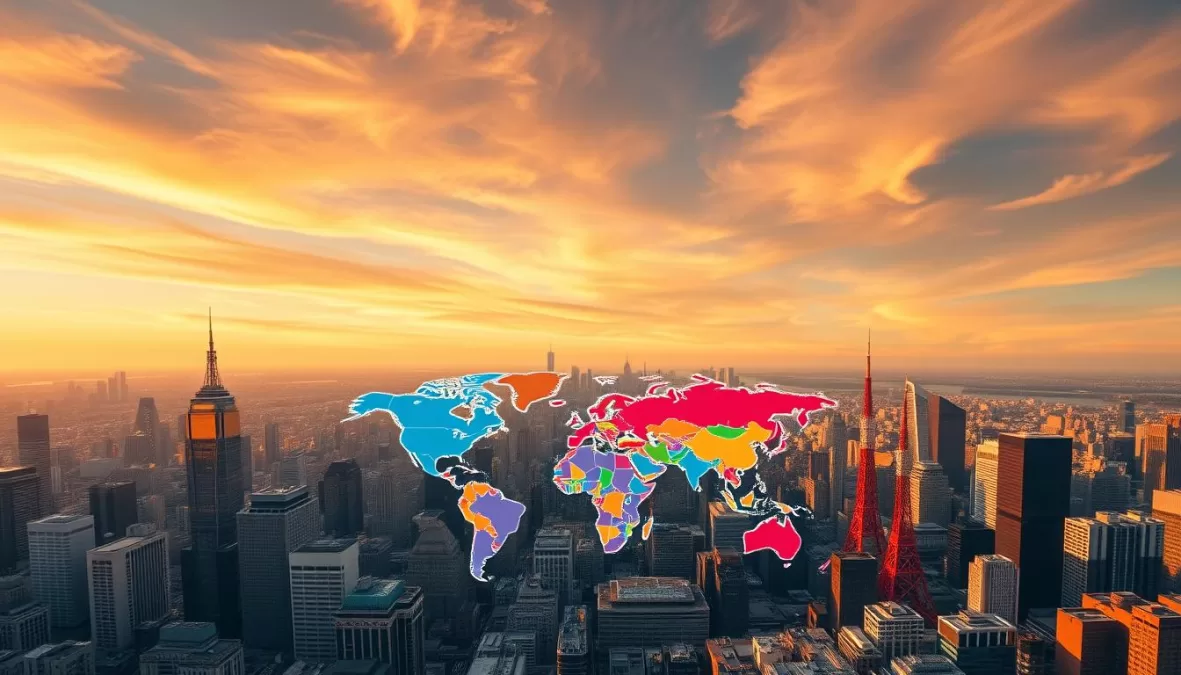
The global economy is dominated by a few powerful nations that contribute significantly to the world’s GDP. Currently, the United States holds the top position with a GDP of $30.507 trillion. However, experts predict that China will soon surpass the US as the world’s largest economy.
The global economic landscape is constantly evolving, with various factors influencing the rankings of the world’s largest economies. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) provides crucial data on nominal GDP, helping us understand the economic strengths and challenges faced by these nations.
Key Takeaways
- The US currently holds the position of the world’s largest economy.
- China is predicted to surpass the US in the near future.
- Nominal GDP is a key indicator of a nation’s economic size.
- The IMF provides crucial data on global economies.
- The global economic landscape is constantly evolving.
- Economic strengths and challenges vary among the world’s largest economies.
Understanding Global Economic Rankings
Economic rankings are crucial for understanding the global economic landscape, as they provide insights into a country’s economic health and influence.
The size of an economy is typically measured by its Gross Domestic Product (GDP), which encompasses the total production of goods and services within a country.
What Defines an Economy’s Size?
An economy’s size is defined by its GDP, which is influenced by factors such as consumer spending, government expenditure, and net exports. A higher GDP generally indicates a larger economy.
The Importance of GDP Measurements
GDP measurements provide crucial insights into a country’s economic health and global economic influence. GDP per capita offers a more nuanced view by accounting for population size, revealing the average economic output per person.
How GDP Is Calculated
Understanding how GDP is calculated is crucial for analyzing a country’s economic performance. GDP, or Gross Domestic Product, is a measure of the total value of goods and services produced within a country’s borders over a specific time period.
The GDP Formula Explained
The formula for calculating GDP is: GDP = C + I + G + (X – M), where C is consumer spending, I is investment, G is government spending, X is exports, and M is imports. This formula provides a comprehensive picture of a country’s economic activity.
Different Methods of Measuring GDP
There are several methods to measure GDP, including nominal GDP, which uses current market prices, and Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) adjusted GDP, which accounts for differences in the cost of living between countries. Additionally, GDP per capita is calculated by dividing a country’s GDP by its population, providing insights into the standard of living.
| GDP Measurement Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Nominal GDP | Uses current market prices to measure economic output. |
| PPP Adjusted GDP | Adjusts for differences in the cost of living between countries. |
| GDP per Capita | Divides a country’s GDP by its population to indicate average economic output per person. |
By understanding these different methods, economists and policymakers can gain a more nuanced view of a country’s economic performance and make informed decisions.
Top 10 Largest Economy in the World 2025
As we approach 2025, the global economic landscape is witnessing significant shifts in the rankings of the world’s largest economies. The period since 2020 has been marked by considerable changes in the global economic order, driven by the COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent recovery patterns.
Overview of Global Economic Leaders
The world’s top economies are led by countries that have demonstrated robust economic growth and adaptability in the face of global challenges. As of 2025, global GDP has risen to $115.49 trillion, indicating a strong recovery from the pandemic-induced contractions of 2020. The world‘s largest economies are expected to continue their growth trajectory, driven by factors such as technological innovation and government policies.
Shifts in Economic Power Since 2020
Since 2020, there have been notable shifts in the global economic hierarchy. Countries like China and India have made significant strides, with China maintaining its position as the second-largest economy since 2010. India’s remarkable economic growth has enabled it to surpass Japan, securing the fourth position among global economies. The GDP growth rate of these countries has been impressive over the past few years, with some recovering faster than others from the pandemic. Analysis of the latest data reveals that these shifts are driven by factors such as technological adaptation and supply chain restructuring.
United States: The World’s Largest Economy
The United States stands as the world’s largest economy, driven by its robust institutional framework and innovative spirit. The U.S. has a relatively open economy, facilitating flexible business investment and foreign direct investment in the country. It is the world’s dominant geopolitical power and can maintain a large external national debt as the producer of the world’s primary reserve currency.
Key Economic Sectors
The U.S. economy is driven by several key sectors, including technology, finance, and healthcare. These sectors contribute significantly to the country’s GDP and are at the forefront of innovation. The U.S. is also a leader in business investment and foreign direct investment, attracting global talent and capital.
Factors Behind U.S. Economic Dominance
Several factors underpin America’s continued economic dominance, including its strong institutional framework, entrepreneurial culture, and global currency leadership. The U.S. dollar’s status as the world’s primary reserve currency provides significant economic advantages, including lower borrowing costs and global financial influence. Additionally, America’s world-class higher education system fosters innovation, research, and a highly skilled workforce, driving economic growth and competitiveness.
- The U.S. economy benefits from open markets and strong property rights protection, attracting global investment.
- America’s business-friendly regulations support entrepreneurship and innovation.
- The country’s GDP per capita is one of the highest among major economies, reflecting its strong economic performance.
China: The Rising Economic Superpower
As the world’s second-largest economy, China is making its mark. China’s economy has seen historical growth in the last two decades, causing some economists to speculate that it may overtake the U.S. as the world’s largest economy in the future.
Manufacturing and Export Strengths
China’s economic growth is largely attributed to its manufacturing and export strengths. The country has become the world’s factory, leveraging its large workforce and infrastructure to produce goods at competitive prices. This has led to significant economic growth, with China’s GDP per capita increasing substantially.
Challenges to Sustained Growth
Despite its impressive economic achievements, China faces several significant challenges. A rapidly aging population and severe environmental degradation are major concerns. China’s high debt levels, particularly in the property sector, pose risks to financial stability.
| Economic Indicator | Value | Growth Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Nominal GDP | $14.34 trillion | 6.1% |
| GDP per capita | $10,260 | 5.5% |
| Export Growth | $2.5 trillion | 4.2% |
China’s transition to a more balanced growth model, driven by domestic consumption, is crucial for sustained growth. However, this transition is challenging, and the country must navigate geopolitical tensions and trade conflicts.
Germany: Europe’s Economic Powerhouse
Europe’s economic powerhouse, Germany, continues to lead through innovation and industrial expertise. With a strong economy driven by manufacturing and exports, Germany plays a vital role in the global world economy.
Industrial Expertise and Export Focus
Germany’s industrial expertise and export-oriented economy make it a significant player in global trade. The country’s highly skilled workforce and innovative manufacturing processes contribute to its growth, maintaining its competitive edge in the global market.
Demographic Challenges
Despite its economic strengths, Germany faces demographic challenges, including an aging population and low fertility rates. These factors strain its social welfare system and impact its gdp. Germany is exploring solutions, including immigration policies, to address these challenges and maintain its economic competitiveness among other countries.
India: The Fastest Growing Major Economy
India’s economic transformation has been remarkable, positioning it as the fastest-growing major economy worldwide. The country’s economy is a blend of traditional village farming, handicrafts, and modern industries, including mechanized agriculture. India’s service sector, particularly technology services and business outsourcing, significantly contributes to its economic output.
Economic Transformation
Since the 1990s, India’s economy has undergone significant liberalization, boosting economic growth. However, challenges such as inflexible business regulations and corruption persist. The GDP growth has been driven by a diverse range of sectors.
Sectors Driving Growth
The service sector accounts for over 50% of India’s GDP, with manufacturing and agriculture playing crucial roles. Key sectors include:
- Information technology and business process outsourcing
- Growing manufacturing sector supported by “Make in India” initiatives
- A massive consumer market driven by a growing middle class
- Emerging growth drivers like digital services, e-commerce, and fintech
These sectors have established India as a global services hub and a major exporter of software services, contributing to its gdp per capita growth.
Japan: Technological Innovation and Economic Resilience
Japan’s economy has shown remarkable resilience in the face of global challenges, driven by its technological innovation. Despite facing significant demographic challenges, Japan continues to be a major player in the global economy.
Manufacturing Excellence and Trade
Japan’s manufacturing sector is renowned for its excellence, particularly in the automotive and electronics industries. The country’s trade policies and agreements have facilitated its export-driven economy, contributing to its GDP growth. Japan’s focus on quality and innovation has enabled it to maintain a competitive edge in the global market.
| Industry | Export Value (Billion USD) | Growth Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | 150 | 5 |
| Electronics | 200 | 7 |
Aging Population Concerns
Japan faces significant challenges due to its rapidly aging population, which threatens its long-term economic sustainability. The declining workforce and increasing healthcare costs pose structural headwinds to economic growth. To mitigate these effects, Japan has been exploring strategies such as increasing automation and encouraging greater labor force participation among women and older workers.

With a GDP per capita of over $40,000, Japan remains one of the world’s leading economies. However, its population dynamics require careful management to ensure continued economic resilience.
United Kingdom: Post-Brexit Economic Landscape
Post-Brexit, the UK’s economy is facing new challenges and opportunities. The nation’s extensive trading relationship with continental Europe has been greatly complicated by the resolution of Brexit after the 2016 vote to leave the European Union (EU). As of January 31, 2020, the U.K. is officially not a member of the EU.
Financial Services Dominance
The UK’s financial services sector remains a significant contributor to its economy. London’s status as a global financial hub has been maintained, with many international financial institutions continuing to operate there. However, the impact of Brexit on the sector is still being assessed, particularly regarding passporting rights that allowed UK-based firms to operate freely in the EU.
Trade Relationship Adjustments
The UK-EU Trade and Cooperation Agreement has introduced new customs procedures and regulatory checks, affecting trade flows. The UK is also pursuing new trade agreements with countries like Australia, New Zealand, and Japan, as well as seeking membership in the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP). This repositioning of the UK’s global trade strategy under the “Global Britain” initiative aims to diversify trade relationships beyond Europe.
| Trade Agreement | Status | Impact on UK Economy |
|---|---|---|
| UK-EU Trade and Cooperation Agreement | Implemented | Increased trade complexity |
| CPTPP Membership | Pursuing | Potential for increased exports |
| Australia-UK Free Trade Agreement | Negotiating | Expected growth in bilateral trade |
“The UK’s decision to leave the EU has presented both challenges and opportunities for its economy. As the country navigates its new trade relationships, it is well-positioned to capitalize on its global connections.”
France: Tourism and Industrial Diversity
France stands out as a global economic leader, thanks to its diverse economy and strong tourism industry. The country’s economy is driven by a mix of industrial sectors, including manufacturing, aerospace, and automotive, alongside a thriving service sector dominated by tourism.
France’s economic structure is characterized by a significant role of government intervention, aimed at promoting social equality. This intervention, however, also presents challenges such as a rigid labor market.
Economic Structure and Government Role
The French government plays a crucial role in the economy through regulations and public spending, which accounts for around 55% of GDP. This significant public expenditure provides comprehensive social benefits but also limits fiscal flexibility.
Social Policies and Economic Challenges
France’s social policies, while beneficial to citizens, contribute to economic challenges such as high unemployment, particularly among young people. Ongoing reforms aim to enhance economic competitiveness while preserving the social model.
- France’s labor market regulations offer strong worker protections but can create hiring rigidities.
- The government is undertaking reforms to improve economic flexibility and fiscal sustainability.
Italy: Regional Economic Disparities
Italy’s economy is characterized by significant regional disparities, with the industrial north driving growth and the southern regions lagging behind. This divide has significant implications for the country’s overall economic performance.
Economic Divide Between North and South
The northern regions of Italy, particularly Lombardy, Piedmont, and Veneto, are hubs of industrial activity, contributing substantially to the country’s GDP. In contrast, southern regions such as Campania, Calabria, and Sicily face challenges related to underdevelopment, high unemployment, and infrastructure deficiencies.
| Region | GDP Per Capita (€) | Unemployment Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Lombardy | 38,400 | 5.5 |
| Campania | 17,300 | 20.4 |
| Veneto | 34,600 | 6.1 |
| Calabria | 15,600 | 23.1 |
Persistent Economic Challenges
Italy’s economy faces several persistent challenges, including a high public debt exceeding 150% of GDP, an inefficient judicial system, and a weak banking sector. These issues hinder economic growth and limit the country’s potential. The government must address these challenges to foster a more favorable business environment and stimulate economic development.
Canada: Natural Resources and Trade Relations
Canada’s economy is significantly influenced by its natural resources and trade relations, particularly with the United States. The country’s vast energy reserves and diverse trade agreements have positioned it as a key player in the global economy.
Energy Sector Strengths
Canada’s energy sector is a significant contributor to its economy, with vast reserves of oil and natural gas. The sector’s strength is driven by advanced extraction technologies and a skilled workforce, making Canada one of the world’s leading energy producers.

U.S.-Canada Economic Integration
The U.S.-Canada economic relationship is one of the world’s most comprehensive trading partnerships. The United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) facilitates cross-border trade and investment, with approximately 77% of Canadian exports heading to the U.S. market. This close economic integration has created both opportunities and challenges for Canada’s economy.
Brazil: South America’s Largest Economy
As the economic powerhouse of South America, Brazil has been on a path of recovery since 2017. Brazil’s economy is diverse, with significant contributions from various sectors.
Diverse Economic Sectors
Brazil’s economy is driven by a mix of agriculture, mining, manufacturing, and services. The country is rich in natural resources, making it a leading producer of commodities. This diversity helps stabilize the economy during fluctuations in global markets.
Recovery and Reform Efforts
Brazil has implemented several economic reforms to boost growth and improve its business environment. Measures include reducing bureaucracy, simplifying the tax system, and investing in infrastructure. These efforts aim to enhance competitiveness and attract foreign investment, ultimately contributing to a higher GDP per capita.
- Brazil has been working to recover from economic and political turbulence.
- The country has implemented reforms aimed at restoring economic growth and fiscal sustainability.
- Efforts to address fiscal challenges include the spending ceiling amendment and pension reform.
India’s GDP Growth Trajectory
With a GDP growth rate of 8.2%, India is climbing the global economic rankings. After recovering from the pandemic-induced slowdown, India’s economy is now on a strong growth trajectory.
Historical Growth Patterns
India’s economic growth has been driven by various sectors, including agriculture, business, and others. The country’s GDP growth rate has been consistently high, making it one of the fastest-growing major economies. Different sectors contribute significantly to employment, driving growth and development.
Projections for 2025 and Beyond
Economic projections indicate that India is poised to continue its strong growth trajectory through 2025 and beyond. The IMF projects India’s GDP growth to remain above 6% annually through the latter half of the decade. Key drivers include:
- Infrastructure development under the National Infrastructure Pipeline
- Production-linked incentive schemes to boost manufacturing
- Digital public infrastructure expansion
India’s economic rise is likely to reshape global economic hierarchies, with projections suggesting it will become the world’s third-largest economy within the next few years.
Factors Influencing Future Economic Rankings
Several critical factors will determine the future landscape of the world’s largest economies. As the global economy continues to evolve, understanding these influences is crucial for predicting shifts in economic power.
Technological Innovation and Digital Transformation
Technological innovation and digital transformation are key drivers of economic growth. The adoption of emerging technologies like AI, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) will significantly impact the competitiveness of nations. As digitalization accelerates, economies that invest heavily in technology infrastructure and talent will likely surge ahead in global rankings.
Climate Change and Sustainable Development
Climate change and the transition to sustainable development models are becoming increasingly important. The global shift toward decarbonization presents both challenges and opportunities. Fossil fuel-dependent nations face transition risks, while leaders in clean technology stand to benefit. As the world moves toward renewable energy and sustainable practices, economies that adapt quickly will gain a competitive edge.
“The transition to a sustainable economy is not just an environmental imperative, but a significant economic opportunity.”
Conclusion
The global economy is undergoing significant changes, with emerging economies challenging the dominance of established powers. As of 2025, the top 10 largest economies in the world showcase a diverse mix of countries, with the United States and China leading the way. India’s economy has shown remarkable growth, securing the fifth position in the World GDP Ranking 2025 list. According to IMF projections, India is poised to overtake Japan and become the fourth largest economy by 2026. The future economic landscape will be shaped by factors like technological innovation, demographic trends, and climate change adaptation. While GDP rankings provide valuable insights, they are just one measure of an economy’s health. Sustainability, inclusivity, and quality of life are equally important considerations for truly successful economies.